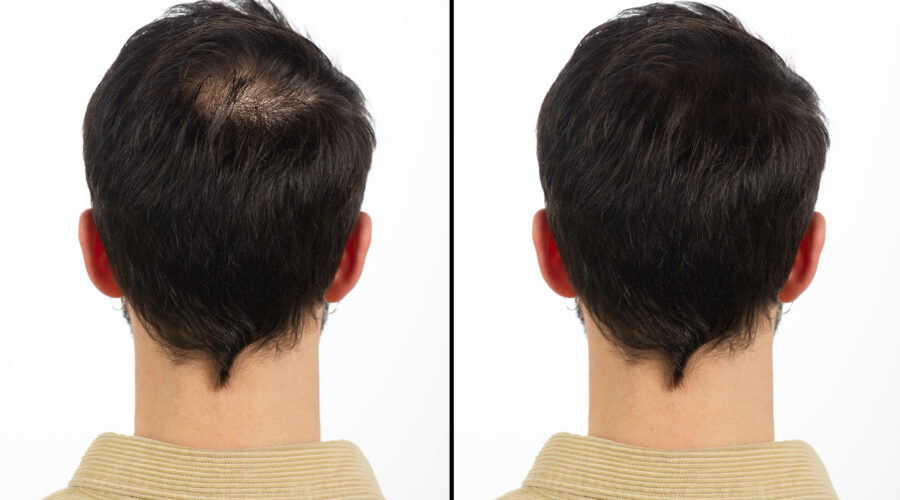
Hair transplants are the only treatment that can permanently treat an area of alopecia.
Androgenic alopecia affects up to 50% of men and women throughout their lives.
Only surgery can permanently and definitively treat an area of hair loss.
Nowadays, the surgical treatment of alopecia, particularly androgenic alopecia (AGA), primarily relies on autografting techniques such as FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction), FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation), and FUL (Follicular Unit Long hair).
The principles of follicular unit transplantation: FUE and FUT (strip method).
Baldness (in both men and women) is due to the sensitivity of hair follicles (the origin of the hair) to a hormone: dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone.
It is the exposure of the follicles to DHT that prevents their regeneration, leading to permanent hair loss. Not all follicles are sensitive to this hormone. The hairs of the crown (the hairline around the head) are not sensitive to DHT and therefore do not fall out, even with age.
The principle of hair transplantation is to implant hairs from the back of the head, which are not sensitive to DHT, into the balding area. Once the transplant has taken, these hairs, which are not susceptible to androgenic alopecia, will no longer fall out.
There is no risk of rejection because it is an autologous transplant.

The Procedure for the FUE Procedure
The first step: follicular unit extraction.
After prior local anesthesia, follicular units, each containing 1 to 4 hairs, are extracted from the donor area. Extraction is performed using a micro-punch less than 1 mm in diameter, which leaves no scar.
The second step: implantation of the hair grafts through micro-incisions. The advantages of FUE hair micrografts:
non-invasive microsurgery
, no scarring in the donor area,
no bleeding,
no pain,
no swelling,
no damage to the hair follicle (minimal transection rate),
limited downtime (1 to 3 days)
natural-looking results
, increased density, and
the possibility of correcting beard growth and scars in these areas (upper lip, chin, etc.) and around the eyebrows.
The FUT (Strip)
The procedure involves taking a strip of scalp from the back of the head (occipital region) and then extracting the follicular units under a microscope. The donor area is then closed using the trichophytic technique (NATAF) so that the hair grows back through the scar and conceals it.
Implantation is performed in the same way as for FUE. The procedure time is shorter, but there is a scar at the back of the head (occipital region).
Sequences and results
The results are very natural; the remote assessment will allow us to evaluate the possibility of additional sessions depending on the density achieved and each patient's wishes.
Final results are assessed after one year.
Complementary treatments Medical treatments
Minoxidil lotion (the only topical treatment) and finasteride (oral treatment) are not 100% effective; they generally stop hair loss but do not restore lost hair. Their effect diminishes after 24 months.
Furthermore, any gains achieved are quickly lost when treatment is discontinued.
It is recommended to combine treatment, generally minoxidil, before and after the transplants. Applying it twice a day slows hair loss by improving local blood flow. This enhances the recipient site for the grafts. The
procedure is performed on an outpatient basis: admission in the morning and discharge the same day. A follow-up appointment is scheduled 48 hours and 10 days post-operatively. It is a relatively painless procedure; medication with paracetamol (Doliprane) is sufficient. In the case of FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): only slight sensitivity may occur in the donor and recipient areas.
In the case of FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): occipital tension may occur due to the strip harvesting.
The graft takes 2-3 days, after which a gentle shampoo is possible. Social downtime varies from 1 to 7 days depending on the technique used and the extent of the procedure.
There are few complications:
bleeding may occur at one of the donor or graft sites, requiring only simple pressure.
Superinfection is very rare and generally localized.
